Application of sensors in the medical industry
Sensors have a wide range of applications in the medical industry, covering the entire process from disease diagnosis and treatment to patient rehabilitation. Here are some of the main application areas:
1. Vital Signs Monitoring: Sensors can monitor patients’ vital signs in real time, such as heart rate, blood pressure, body temperature, and blood oxygen saturation. This data provides medical staff with real-time and accurate information to help them make timely medical decisions. For example, oximeters use infrared light technology to monitor blood oxygen saturation, which is particularly critical for patients with respiratory diseases.
2. Medical Equipment Monitoring: Sensors can monitor the status of medical equipment to ensure the normal operation and safety of medical equipment. For example, in the operating room, sensors can monitor environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and air pressure to provide optimal conditions for surgery.
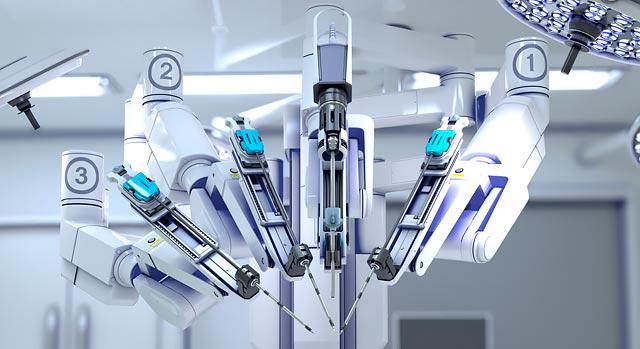
3. Minimally Invasive Surgery Assistance: In minimally invasive surgery, sensors can help doctors accurately position and operate, improving the success rate and safety of surgery. For example, in endoscopic surgery, sensors can assist doctors in precise cutting and suturing.
4. Rehabilitation Equipment Monitoring: In physical therapy and rehabilitation equipment, sensors are used to monitor patients’ movements and rehabilitation progress, provide feedback to doctors, and help them develop personalized rehabilitation plans.
5. Drug monitoring and management: Sensors can be used to monitor the infusion volume and flow rate of drugs to ensure the accuracy and safety of drug delivery. In addition, sensors can also monitor patients’ drug reactions and side effects, helping doctors to adjust treatment plans in a timely manner.
6. Health management: New biosensors can monitor changes in chemical substances in the human body in real time, such as blood sugar, blood oxygen, heart rate, etc., and transmit data to mobile phones or computers for analysis and processing. This enables people to manage their health more conveniently and adjust their lifestyles and eating habits in a timely manner.
In general, the application of sensors in the medical field has greatly improved the efficiency and accuracy of medical work and provided patients with a better diagnosis and treatment experience. With the continuous advancement of technology, the application of sensors in the medical industry will be more extensive and in-depth.






